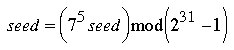
Y = rand(n)Y = rand(m,n)Y = rand(size(A))rand('seed')rand('seed',n)rand
rand generates random numbers and matrices whose elements are uniformly distributed in the interval (0,1).
rand(n) is an n-by-n matrix with random entries.
rand(m,n) is an m-by-n matrix with random entries.
rand(size(A)) is the same size as A and has random entries.
rand('seed') returns the current value of the seed used by the generator.
rand('seed',n) sets the seed to n. rand('seed',0) sets the seed to its startup value.
rand with no arguments is a scalar whose value changes each time it is referenced.
The functions rand and randn maintain separate generators with separate seeds.
rand has not yet been used during a particular MATLAB session, then R = rand(3,4) produces
A random choice between two equally probable alternatives can be made withR =0.2190 0.6793 0.5194 0.05350.0470 0.9347 0.8310 0.52970.6789 0.3835 0.0346 0.6711
if rand < .5'heads'else'tails'end
rand is a uniform random number generator based on the linear congruential method described in [1]. The basic algorithm is
randn,randperm
(c) Copyright 1994 by The MathWorks, Inc.