x = 1900:1:2000;
y = spline(t,p,x);
plot(t,p,'o',x,y)
title('United States Census')
xlabel('year')
yi = spline(x,y,xi)pp = spline(x,y)
spline interpolates between data points using cubic spline fits.
yi = spline(x,y,xi) accepts vectors x and y that contain coarsely spaced data, and vector xi that specifies a new, more finely spaced abscissa. The function uses cubic spline interpolation to find a vector yi corresponding to xi.
pp = spline(x,y) returns the pp-form of the cubic spline interpolant, for later use with ppval and other spline functions.
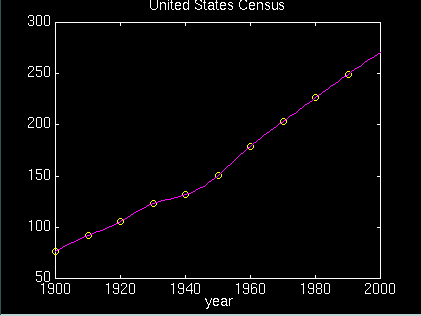
The expressiont = 1900:10:1990;p = [ 75.995 91.972 105.711 123.203 131.669 ...150.697 179.323 203.212 226.505 249.633 ]';
spline(t,p,2000)
uses the cubic spline to extrapolate and predict the population in the year 2000. The result is
The following statements interpolate the data with a cubic spline, evaluate that spline for each year from 1900 to 2000, and plot the result.ans =270.6060
x = 1900:1:2000;y = spline(t,p,x);plot(t,p,'o',x,y)title('United States Census')xlabel('year')
spline is a MATLAB M-file. It uses the M-files ppval, mkpp, and unmkpp. These routines form a small suite of functions for working with piecewise polynomials. spline uses these functions in a fairly simple fashion to perform cubic spline interpolation. For access to the more advanced features, see the M-files and the Spline Toolbox.
interp1,polyfit
(c) Copyright 1994 by The MathWorks, Inc.